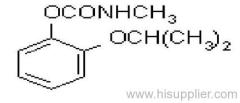
Common name: propoxur
IUPAC name: 2-isopropoxyphenyl methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name: 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl methylcarbamate
CAS RN: [114-26-1]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt.: 209.2; M.f.: C11H15NO3; Form: Colourless crystals; (tech., white to cream-coloured crystals). M.p.: 90 ºC (crystal form I), 87.5 ºC (crystal form II, unstable). B.p.: Decomposes on distillation. V.p.: 1.3 mPa (20 ºC); 2.8 mPa (25 ºC). KOW: logP = 1.56; Henry: 1.5x10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C). S.g./density: 1.18 (20 ºC). Solubility: In water 1.9 g/l (20 ºC). Soluble in most organic solvents, e.g. isopropanol >200, toluene 50-100, hexane 1-2 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability: Stable in water at pH 7. Hydrolysed by strong alkali; DT50 (22 ºC) 1 y (pH 4), 93 d (pH 7), 30 h (pH 9); DT50 (20 ºC) 40 min (pH 10). Direct photodegradation is not a major contributor to the overall elimination of propoxur from the environment (DT50 5-10 d); indirect photodecomposition (addition of humic acid) is more rapid (DT50 88 h).
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry: Cholinesterase inhibitor.
Mode of action: Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Gives rapid knockdown, and has long residual activity.
Uses: Control of cockroaches, flies, fleas, mosquitoes, bugs, ants, millipedes and other insect pests in food storage areas, houses, animal houses, etc. Control of sucking and chewing insects (including aphids) in fruit, vegetables, ornamentals, vines, maize, alfalfa, soya beans, cotton, sugar cane, rice, cocoa, forestry, etc.; also against migratory locusts and grasshoppers.
Phytotoxicity: Chrysanthemums, carnations, and hydrangeas may be injured at higher dose rates. Blossom thinning may occur on fruit trees.
Formulation types: AE; DP; EC; FU; GR; RB; SL; UL; WP; Oilspray.
Compatibility: Mixtures with alkaline substances are not stable.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral: Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats c. 50 mg/kg.
Skin and eye: Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits).
Inhalation: LC50 for rats (4 h) >0.5 mg/l (aerosol); 0.654 mg/l air (dust).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats 200, mice 500 mg/kg diet; (12 mo) for dogs 200 mg/kg diet.
ADI: 0.02 mg/kg b.w.
Toxicity class: WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II
EC hazard: T; R25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds: Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail 2828, mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet.
Fish: LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 6.2-6.6, rainbow trout 3.7-13.6, golden orfe 12.4 mg/l.
Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 0.15 mg/l.
Bees: Highly toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: In rats, the principal metabolites are 2-hydroxyphenyl-N-methylcarbamate and 2-isopropoxyphenol; minor metabolites include 5-hydroxy propoxur and N-hydroxymethyl propoxur. Elimination is very rapid, 96% excreted in the urine. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed.
Plants: The primary metabolite is demethyl propoxur (max. amount 2.7-3.6%).
Soil/Environment: The mobility of propoxur in the soil is relatively high. The compound rapidly degrades in different soils.